Table of Contents
- Understanding Load Capacity
- Assessing Floor Conditions
- Evaluating Environmental Factors
- Choosing the Right Wheel Material
- Considering Wheel Diameter and Width
- Understanding Bearing Types
- Factoring in Speed and Maneuverability
- Maintenance and Durability
- Conclusion
Choosing the right wheels for your material handling equipment is critical for optimizing your operations, ensuring workplace safety, and extending equipment lifespan. The best wheels will enhance maneuverability, safeguard your flooring, and reduce ongoing maintenance costs. With options like stainless steel caster wheels, you can equip your facility to handle various operational demands and harsh environments. The right selection also minimizes workplace injuries and maximizes production efficiency—factors every business should prioritize.
Beyond durability, the wheels you choose play a significant role in protecting your facility’s floors and adapting to your unique conditions. After all, the wrong wheel can lead to costly repairs and inconvenient downtime. This comprehensive guide explores the key factors to consider, enabling you to make an informed, cost-effective decision tailored to your facility’s needs.
Understanding Load Capacity
Before selecting wheels, assess the total weight of your equipment and loads to prevent overloading, which may cause premature wear and accidents. To determine wheel load requirements, sum the equipment weight and maximum load, divide by the number of wheels, and include a safety margin for uneven terrain. For instance, for a 2,000-pound setup with four wheels, each should be rated for at least 500 pounds, plus a safety buffer, as underestimating load capacity is a frequent mistake.
Assessing Floor Conditions
The surfaces your equipment traverses will dictate the ideal wheel properties. Hard, smooth floors like concrete or tile benefit from harder wheel types, which generate less rolling resistance and reduce physical strain on staff. For rough, uneven, or delicate surfaces, opt for softer wheels to minimize vibration, protect flooring, and improve grip.
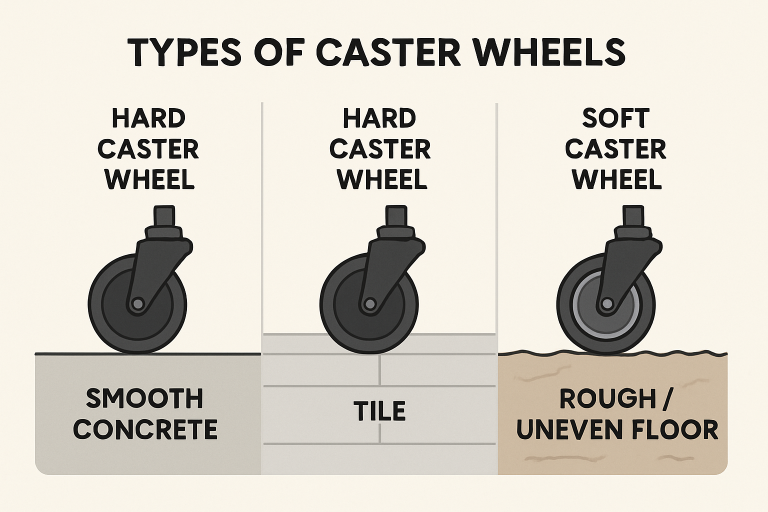
Matching wheel hardness and tread material to the floor type can prevent unsightly marks, prolong floor lifespan, and ensure smooth, safe movement for both manual and powered handling equipment. Facilities with mixed or irregular surfaces should consider multi-surface or non-marking wheels for maximum versatility.
Evaluating Environmental Factors
Factor in ambient conditions, exposure to chemicals, temperature extremes, and wet areas when selecting wheels. If wheels are expected to encounter oils, cleaning agents, or moisture, select materials like nylon or stainless steel that are resistant to corrosion and chemical attack. In temperature-controlled settings or outdoor environments, verify wheels’ temperature ratings to ensure reliable performance and safety.
Ignoring environmental factors can lead to premature failure, corrosion, and increased maintenance. Consider how often your wheels will be exposed to water, aggressive cleaning, or outdoor elements, and prioritize options with enhanced resilience for long-term savings.
Choosing the Right Wheel Material
Different wheel materials offer specific advantages for durability, floor protection, and load handling. Polyurethane is versatile, suitable for various surfaces. Nylon excels in chemical and moisture-rich environments, being resistant and easy to clean. Rubber ensures smooth operation and shock absorption for fragile loads on uneven surfaces. Steel is suitable for heavy-duty applications and harsh conditions, but can damage delicate floors. Selecting the appropriate material depends on priorities such as floor longevity, equipment life, and ease of movement.
Considering Wheel Diameter and Width
Bigger wheels make it easier to roll equipment over thresholds, debris, or rough flooring. Larger diameters improve load distribution and decrease the force required for movement, reducing the risk of worker fatigue and injury. Wider wheels lower the risk of floor damage by spreading the load over a greater surface area, enhancing stability, especially for tall or top-heavy equipment. Be sure to assess your equipment’s clearance and workspace dimensions before deciding on wheel size.
Understanding Bearing Types
Wheel bearings are crucial for ensuring maneuverability, load handling, and efficient movement. The main types include: Plain Bearings, which are affordable and suited for light loads with infrequent use; Ball Bearings, which provide high efficiency and quiet operation, making them suitable for frequent use or heavier loads; and Roller Bearings, designed for maximum load capacity but requiring more maintenance. When selecting a bearing type, consider the load weight and frequency of equipment use, as higher-quality bearings can lead to reduced push-pull force and an extended operational lifespan.
Factoring in Speed and Maneuverability
The design and material of your chosen wheels also influence speed, control, and turning radius. For fast-moving equipment or frequent directional changes, opt for wheels with precision bearings and heat-resistant materials. If your operation requires both straight-line tracking and agile turns, consider a combination of fixed and swivel casters to leverage the benefits of both stability and flexibility.
Maintenance and Durability
Scheduled inspections and preventive maintenance are crucial for identifying issues such as cracked, worn, or debris-clogged wheels before they lead to failures. Wheels made from materials like polyurethane and nylon offer greater resistance to abrasion and chemical damage, enabling longer service intervals. Investing in high-quality wheels can lower replacement frequency and costs, providing long-term value. When selecting the appropriate wheels for material handling equipment, consider specific environmental conditions, operational requirements, and safety factors to ensure efficient performance, minimize downtime, and enhance workplace safety and productivity.
Conclusion
Selecting the right wheels for material handling equipment requires a balanced evaluation of load capacity, floor conditions, environmental exposure, and operational demands. By carefully considering wheel material, size, bearings, speed requirements, and maneuverability, organizations can enhance efficiency while minimizing strain on both equipment and personnel. Just as important, routine maintenance and informed material choices help prevent premature failures, protect flooring, and control long-term costs. When these factors are addressed together, wheel selection becomes a strategic decision that supports safer operations, smoother movement, and sustained productivity across diverse work environments.